Multithreading is the ability of a program or an operating system to enable more than one user at a time without requiring multiple copies of the program running on the computer. Multithreading can also handle multiple requests from the same user.
The concept of multi-threading needs proper understanding of these two terms – a process and a thread. A process is a program being executed. A process can be further divided into independent units known as threads. A thread is like a small light-weight process within a process. Or we can say a collection of threads is what is known as a process.
A thread is a path which is followed during a program’s execution. Majority of programs written now a days run as a single thread. Lets say, for example a program is not capable of reading keystrokes while making drawings. These tasks cannot be executed by the program at the same time. This problem can be solved through multitasking so that two or more tasks can be executed simultaneously.
Multitasking is of two types: Processor based and thread based. Processor based multitasking is totally managed by the OS, however multitasking through multithreading can be controlled by the programmer to some extent.
What is a Thread in Programming?
A thread is an independent unit of execution created within the context of a process (or application that is being executed). When multiple threads are executing in a process at the same time, we get the term “multithreading.” Think of it as the application’s version of multitasking.
Definition of Thread.
What is Threading ?
Threading is a segment which divide the code into small parts that are of very light weight and has less burden on CPU memory so that it can be easily worked out and can achieve goal in desired field. The concept of threading is designed due to the problem of fast and regular changes in technology and less the work in different areas due to less application. Then as says “need is the generation of creation or innovation” hence by following this approach human mind develop the concept of thread to enhance the capability of programming.
Applications – Threading is used widely in almost every field. Most widely it is seen over the internet nowadays where we are using transaction processing of every type like recharges, online transfer, banking etc.
Lifecycle of a thread :
There are various stages in the lifecycle of a thread. Following are the stages a thread goes through in its whole life.
- New: The lifecycle of a born thread (new thread) starts in this state. It remains in this state till a program starts.
- Runnable: A thread becomes runnable after it starts. It is considered to be executing the task given to it.
- Waiting: While waiting for another thread to perform a task, the currently running thread goes into the waiting state and then transitions back again after receiving a signal from the other thread.
- Timed Waiting: A runnable thread enters into this state for a specific time interval and then transitions back when the time interval expires or the event the thread was waiting for occurs.
- Terminated (Dead): A thread enters into this state after completing its task.
Types of execution in OS
There are two types of execution:
- Concurrent Execution: This occurs when a processor is successful in switching resources between threads in a multithreaded process on a single processor.
- Parallel Execution: This occurs when every thread in the process runs on a separate processor at the same time and in the same multithreaded process
How does multithreading work?
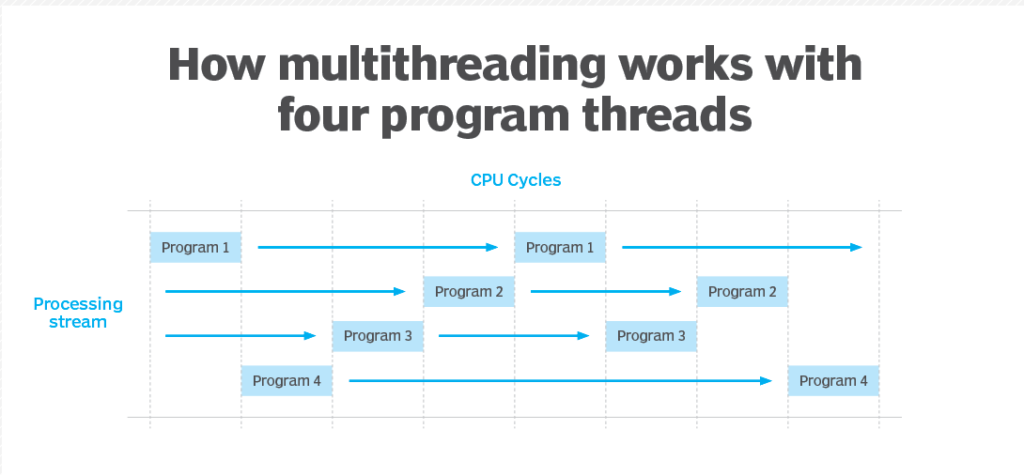
The extremely fast processing speeds of today’s microprocessors make multithreading possible. Even though the processor executes only one instruction at a time, threads from multiple programs are executed so fast that it appears multiple programs are executing concurrently.
Each CPU cycle executes a single thread that links to all other threads in its stream. This synchronization process occurs so quickly that it appears all the streams are executing at the same time. This can be described as a multithreaded program, as it can execute many threads while processing.
Each thread contains information about how it relates to the overall program. While in the asynchronous processing stream, some threads are executed while others wait for their turn. Multithreading requires programmers to pay careful attention to prevent race conditions and deadlock.
Disadvantage of multitasking :
Multithreading is complex and many times difficult to handle. It has a few drawbacks. These are:
- If you don’t make use of the locking mechanisms properly, while investigating data access issues there is a chance of problems arising like data inconsistency and dead-lock.
- If many threads try to access the same data, then there is a chance that the situation of thread starvation may arise. Resource contention issues are another problem that can trouble the user.
- Display issues may occur if threads lack coordination when displaying data.
Advantage of multitasking :
- Multithreading can improve the performance and efficiency of a program by utilizing the available CPU resources more effectively. Executing multiple threads concurrently, it can take advantage of parallelism and reduce overall execution time.
- Multithreading can enhance responsiveness in applications that involve user interaction. By separating time-consuming tasks from the main thread, the user interface can remain responsive and not freeze or become unresponsive.
- Multithreading can enable better resource utilization. For example, in a server application, multiple threads can handle incoming client requests simultaneously, allowing the server to serve more clients concurrently.
- Multithreading can facilitate better code organization and modularity by dividing complex tasks into smaller, manageable units of execution. Each thread can handle a specific part of the task, making the code easier to understand and maintain.
Multithreading vs. multitasking vs. multiprocessing
- Multithreading is a model of program execution that allows for multiple threads to be created within a process, executing independently but concurrently sharing process resources. Depending on the hardware, threads can run fully parallel if they are distributed to their own CPU core.
- Multitasking is a computer’s ability to execute two or more concurrent programs. Multithreading makes multitasking possible when it breaks programs into smaller, executable threads. Each thread has the programming elements needed to execute the main program, and the computer executes each thread one at a time.
- Multiprocessing uses more than one CPU to speed up overall processing and supports multitasking.
Thanks for being here.


Pingback: MSCCS-104 (Assignment : July-2023, Jan-2024) – RajCTU